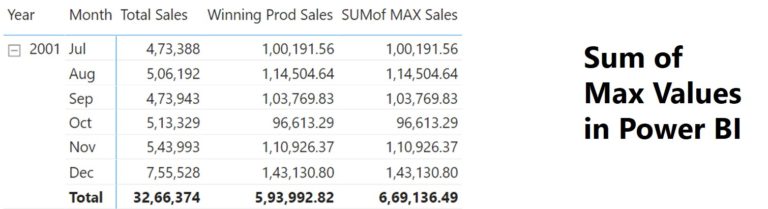
Vanilla SUM and MAX calculations are pretty straightforward in Power BI. But every once in a while you may come across slightly twisted calculation such as find the MAX value and then SUM them. In this post, I will discuss how to find the SUM of MAX values in Power BI. Sum of Max Values in Power BI – Video Consider the following Data I have Calendar, Customers and Products tables linked to the Sales table via one to many relationship. I also have a pivot table displaying the sales by year and by month. Now, I want to find the sales of MAX selling product each month inside the pivot table. Calculating MAX Sales by Product for each Month. This can be done by creating a new measure as follows: Winning Prod Sales = MAXX ( Products, [Total Sales] ) Dragging this measure to the pivot table, I’ll be able to see the following result. The year total shows the Sales of MAX Selling product for the entire year, however, I want to the sum of all the MAX Selling Products for each Month at the total level. Calculating SUM of MAX Values Here is the broad logic to solve this. I need to capture monthly max values at the total level and then sum them. To solve this I will create a new measure as follows: SUMof MAX Sales = SUMX ( ADDCOLUMNS ( SUMMARIZE ( — Summary table to get monthly level granularity Sales, ‘Calendar'[Year], ‘Calendar'[Month] ), “MAXSales”, MAXX ( — for each month calculating MAX Selling Product Products, [Total Sales] ) ), [MAXSales] ) Drag this measure to the pivot table. Now, the pivot table will display the SUM of MAX Values at the total level. More on DAX Display Table or Matrix Until the Selected Date Fiscal Year Date Table in Power BI Display Top N items and Others in Power BI Change Measures Using a Slicer in Power BI